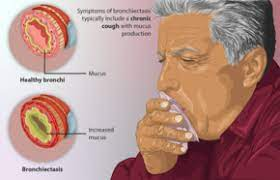
Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung condition in which the bronchial tubes become widened, leading to the accumulation of mucus and increased susceptibility to infection. Symptoms include persistent cough, shortness of breath, and frequent lung infections. The condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including cystic fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and autoimmune disorders. Treatment options include antibiotics to treat infections and bronchodilators. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged areas of the lungs. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan.
Lung infections
Lung infections refer to infections that affect the respiratory system, the lungs. Some common types of lung infections include pneumonia, bronchitis, and tuberculosis. Symptoms can include cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, and fever. Treatment options may include antibiotics, antiviral medications, and supportive care. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a lung infection.
Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath, also known as dyspnea, is a feeling of difficulty breathing or not getting enough air. It can be a symptom of a wide range of conditions, including asthma, pneumonia, heart failure, lung cancer, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It can also be caused by anxiety or panic attacks. If shortness of breath is severe or accompanied by chest pain, it's important to seek medical attention immediately, as it could be a sign of a heart attack. If you are experiencing shortness of breath, it is important to talk to your doctor to determine the cause and best course of treatment.
Including asthma
Asthma is a chronic lung condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, which can lead to difficulty breathing, wheezing, and coughing. It is treated with inhaled medications, such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids, as well as. In severe cases, oral medications and oxygen therapy may also be used.
Wheezing
Wheezing is a whistling or whistling sound when breathing, due to narrowed or obstructed airways. It can be caused by a variety of conditions, including asthma, bronchitis, and emphysema. If wheezing is accompanied by difficulty breathing, chest tightness, or other symptoms.
Bronchitis
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from the lungs. Symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. Acute bronchitis is usually caused by a viral infection and resolves on its own within a few weeks, while chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition caused by exposure to irritants such as cigarette smoke and air pollution. Treatment for bronchitis may include rest, over-the-counter medications to reduce
Symptoms
The main symptoms of bronchitis are:
- Cough, which may produce mucus (sputum)
- Shortness of breath and chest tightness
- Fatigue
- Slight fever and chills
- Occasional wheezing or a whistling sound when breathing
- Chest discomfort
- Headaches
- Sore throat
- Body aches
Symptoms of acute bronchitis usually last for several days to a couple of weeks, while symptoms of chronic bronchitis can persist for months to years. If you have a fever, difficulty breathing, chest pain, or a cough that produces blood, you should seek medical attention immediately.


Comments
Post a Comment