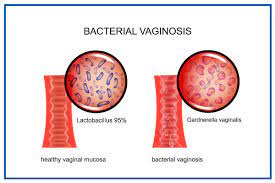
Bacterial vaginosis: An update on diagnosis and treatment
Treatment of BV
Despite extensive therapeutic research, BV remains difficult to treat, and clinicians are ill-equipped to treat BV in the long term. Furthermore, the evaluation of available evidence. BV treatment options are hampered by methodological problems.
The basis of BV treatment
Treatment for BV is aimed at resolving or reducing symptoms, usually a foul-smelling discharge. BV can resolve on its own without treatment; but, it often recurs over a long period. Because BV recurrence is common, treatment for BV also focuses on preventing BV recurrence. Secondary BV treatment aims to prevent BV-related infectious complications and so includes treatment of asymptomatic BV.
Meaning of treatment
The evaluation of the therapeutic effectiveness of a given treatment depends on the clinical context. Such an assessment will be made. In clinical practice, BV treatment is usually considered correct if the patient reports treatment-induced resolution of symptoms during follow-up visits. In contrast to this symptomatic approach, a more aimed way to determine treatment is to reassess using the Amsel [1] or Nugent criteria. [3]
This approach is not well defined, so there is some ambiguity. If treatment is assessed according to Amsel's criteria, treatment is acceptable if no more than. Two symptoms are present according to Amsel et al. [1] Continue therapy because at least three of the four symptoms are required to establish the diagnosis. Most researchers agree that clinical. Treatment is seen in the resolution of all of Amsel's symptoms. microbiological cure as assessed by Nugent's criteria [3] is not defined: does microbiological cure state resolution of BV, i.e. Nugent score below 7, or should it be reversed? normal microflora, is less than 4 points? Both definitions have been used in the literature. The difference between the two conditions is very important because of the previous definition. The transformation of the normal microflora with a score of less than 7, can lead to a normal microflora (Nugent score 4-6). While the intermediate microflora is defined as a more normal microflora with a score of less than 3. BV is likely to pass.
Another aspect of treatment evaluation that has not yet been determined concerns the time involved in therapy. Many studies report the extent of treatment by assessing patients after discontinuation of treatment or at a 1-week follow-up. Only a small number of studies report the treatment as defined by Amsel or Nugent criteria for 3-4 weeks. As more than 50% of women can have persistence or relapse within 2 months of antibiotic treatment, [52]. Evaluation of treatment in long-term follow-up for example can be a good indicator of therapeutic efficacy. But very few studies have adopted this approach. Currently, the only guidance for evaluating post-treatment BV treatment comes from a draft guidance document launched by the US FDA. [53] According to these guidelines, the cure is defined as the absence of all four symptoms. Amsel and a score of less than 4 in the cure test 21-30 days after the first day of treatment. This rigorous approach is gaining more attention from researchers in the field as a standard to determine the treatment of BV.
Treatment methods
Antibiotics have been the mainstay of BV treatment for the past six decades. But, some alternative approaches deserve attention and can be categorized as treatment. With antiseptics and disinfectants, tissue acidifiers or buffering agents, and probiotics, either. As independent therapy or combined with antibiotics.
Standard treatment with antibiotics
After the advent of antibiotics in the 1950s, efforts were made to determine the optimal antibiotic therapy for BV. Several antibiotics were replicated in the following decades, but many of the early therapeutic successes of this period could not be replicated. [54]
Finally, Pheifer et al. In 1978, the New England Journal of Medicine reported that oral metronidazole 500 mg twice daily for 7 days was eliminated. Haemophilus vaginalis in all 81 patients treated with signs and symptoms. [54] 10 years later, Grace et al. found an oral regimen of clindamycin 300 mg twice a day to be safe and effective as the metronidazole regimen. [55] Since then metronidazole and clindamycin.
Comments
Post a Comment